Saturday, December 19, 2009
Wednesday, December 16, 2009
Life of a Star
After thousands of millions of years, the nuclear reactions in the sun will stop. Gravity will then squeeze the core, creating heat that will make the outer layers swell, swallowing Earth. The outer layers will drift into space, leaving a planet-sized star called a White dwarf.
Sunday, December 13, 2009
Formation of Black Holes
Saturday, December 12, 2009
Gravitational Radius
Schwarzschild calculated the relationship between this distance from a body’s center and the mass of the body. This distance is known as the Schwarzschild radius. For bodies such as planets and stars, Schwarzschild’s radius is mush smaller than the body. For example for Earth it is less than one half of an inch, and it is about one and a half miles for the sun.
Schwarzschild’s theory was that a black hole was formed if the gravitational radius of a body was larger than its actual radius. This means a body would have to be squeezed into an extremely tiny space. For example, Earth would have to be squashed to the size of a pea for it to become a Black hole.
Tuesday, December 1, 2009
Theoretical Black Hole
NHXCGTRF55NT
Monday, November 30, 2009
Changing the Rules
Sunday, November 29, 2009
Dark Stars
Friday, November 27, 2009
Light and gravity
Monday, November 23, 2009
Black Hole
In most great mysteries, such as UFOs, science tries to explain the strange things that people claim to have seen. In the case of black holes, however things are the other way around. Scientists predicted the existence of black holes long before there was any real evidence that they existed. In fact, the very nature of black holes means they cannot be seen to be believed!
Thursday, November 19, 2009
Varying Heights
Tuesday, November 17, 2009
Life in the slow lane
In 1905, long before we started flying in space. Einstein knew the speed of light never changes as it is constant. Time however, is relative said Einstein. It can change. It changes according to the speed of what is measuring it. The faster the speed, the slower time passes. In fact, a very accurate clock aboard a space shuttle was measured after its return to Earth it lost 2.95 x 10^-10 seconds for each second of the trip. If the shuttle had been traveling near the speed of light and had been gone for several years, the time loss would have been bigger. So if you went on a very long space trip and our space craft could travel close to speed of light we would be younger than our current same-age friends when we returned to Earth.
Sunday, November 15, 2009
Weight on different Planets
Mercury ----- x .38 =
Venus ----- x .91 =
Earth ----- x 1.00 =
Mars ----- x .38 =
Jupiter ----- x 2.34 =
Saturn ----- x .93 =
Uranus ----- x .79 =
Neptune ----- x 1.14 =
Pluto ----- x .04 =
Thursday, November 12, 2009
Relative theory of Einstein
Einstein’s other great theory, the special Theory of relativity, predicted that the passing of time and the measurement of distance change as movement becomes faster and faster. The effects of this become noticeable only as the speed of light is approached. This would have the consequences for black holes, since objects that fall into black holes would begin to go as fast as the speed of light.
Tuesday, November 10, 2009
Mass and Weight
Friday, November 6, 2009
Escape Velocity
Wednesday, November 4, 2009
Astrophysics
Monday, November 2, 2009
Nature of light
Friday, October 30, 2009
Gravity
This is called the Law of Universal Gravitation. It was first written by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727). This law of gravity explains how the gravitational pull between bodies causes the planets to orbit the sun. A body has a gravitational field around it. Any other object in the field experiences a pull from the body, which pulls the object towards it.
Wednesday, October 28, 2009
Unsolved Mysteries
Saturday, October 24, 2009
Halley
Here’s a timeline that shows some of the world changing events that happened between Halley’s visits. As you will see, Halley doesn’t appear at exactly even intervals. By computing the averages time between visits what year would you except the comet to turn up next?
1338- Hundred Years war starts between England and France on 1301 Visit.
1405- Chinese Sailors explore the Indian Ocean on 1378 Visit.
1492- Columbus sets sail to find a route to Asia through the Pacific.
on 1456 visit.
1910- World War I begins on 1910 visit.
1986- First Official U.S. observation of Martin Luther king Jr. Day, in honor of slain civil rights leader, space shuttle Challenger explodes
Thursday, October 22, 2009
Meteor Master
Jupiter’s gravity had grabbed the comet and forced it to orbit the gas giant instead of the Sun. The powerful gravity ripped the comet into 21 pieces, all of which slammed into Jupiter in 1994. The spectacular crash gave astronomers an exciting glimpse at the chemistry of Jupiter’s mysterious atmosphere.
Tuesday, October 20, 2009
Stick Man
Monday, October 19, 2009
Sunday, October 18, 2009
Hang Ten
Saturday, October 17, 2009
Betelgeuse
Thursday, October 15, 2009
Orion
Tuesday, October 13, 2009
Astrology
Monday, October 12, 2009
Nebula
Big Dipper
Where you are on the earth and how the earth is moving determines which parts of the inside of the sphere you see. As the Earth revolves on its axis, the stars and constellations appear to revolve in the sky around a point directly over the axis. The earth not only revolves on its axis, but it also changes position as it orbits the Sun.
So in late September the Big Dipper will appear low in the sky. And in March of next year, it will appear to be in the same place it was this march.
Sunday, October 11, 2009
Polaris
Friday, October 9, 2009
Thursday, October 8, 2009
BInary Star
Tuesday, October 6, 2009
Neutron Star
Sunday, October 4, 2009
Sirius
Saturday, October 3, 2009
Friday, October 2, 2009
Proxima Centauri
Thursday, October 1, 2009
Wednesday, September 30, 2009
Horsehead Nebula
Tuesday, September 29, 2009
Monday, September 28, 2009
Supernova Remnant
Once it burned bright in the sky and then faded to the glowing rings as shown in the picture.
Sunday, September 27, 2009
Saturday, September 26, 2009
Sombrero Galaxy
Friday, September 25, 2009
Thursday, September 24, 2009
Eta Carinae
Wednesday, September 23, 2009
Tuesday, September 22, 2009
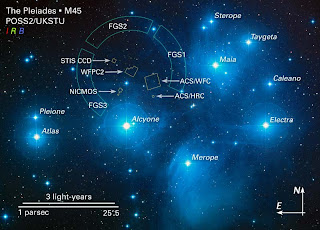
Pleiades Star Cluster
Monday, September 21, 2009
Sunday, September 20, 2009
Megellanic Clouds
The large Megellanic cloud is about 10,000 million stars. The small Megellanic cloud is 2, 30,000 light years away and contains fewer stars. Both clouds contain bright nebulae where new stars are formed.
Friday, September 18, 2009
Types of Galaxies
1. Irregular Shaped,
2. Spiral with trailing arms of stars and nebulae
3. Elliptical.
The spiral and irregular galaxies have both old and young stars and reserves of gas and dust to make new stars. The special ones like our own galaxy Milky Way, has a centre which consists of red giants or dying stars while the new stars are formed in the dusty arms. Elliptical galaxies are supposed to be spiral galaxies that have lost their arms in due course of time. They consist mainly of red giant stars.
Admin says,
As we had an introduction to what is universe. Let me introduce some new terminologies which are unknown to common people in the next post.
Wednesday, September 16, 2009
UNIVERSE
About 300,000 years later, when things cooled, atoms formed. The elements hydrogen and helium were created: Gravity brought them together in clumps. These clumps became the seeds of galaxies. Stars formed, including the Sun, our closest star. It took a long time for the universe to form. Scientists refer to the formation of the universe as the Big Bang theory. Other theories have also been offered, but the Bing Bang has the widest acceptance.
There were no eyewitnesses, so it’s impossible to be absolutely sure what really happened and we probably will never know. It’s unlikely that Big Bang theory, or any other theory, will ever be proved as fact. Our planets revolve around the Sun, and our Solar system moves along the spiral arms of our galaxy, the Milky Way. Gravity holds together this galaxy made up of billions of stars, dust, and gas. The Milky Way is just one of the millions of galaxies scattered across the universe. In between galaxies are enormous voids, or spaces full of nothing.